Dear Friend, Please Copy Link Below, Add Me and Then Buzz on this post Comment to do Link Exchange.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
A Cursor can be imagine as A Table in MySQL PLSQL. We can use a cursor as temp table that we process in the PLSQL.
Below i have a simple MySQLTrigger to show how cursor can be use. I use MySQL version 5.1.33.
Please Just See A Red Row of the Program, That i will Explain.
DELIMITER $$
DROP TRIGGER /*!50032 IF EXISTS */ `db_pengabdian`.`update_jum_pengabdi`$$
CREATE
/*!50017 DEFINER = 'root'@'localhost' */
TRIGGER `update_jum_pengabdi` AFTER UPDATE ON `tb_mketua`
FOR EACH ROW BEGIN
DECLARE done INT DEFAULT 0;
DECLARE nip CHAR(30);
DECLARE yr YEAR;
DECLARE jum INT;
DECLARE cur1 CURSOR FOR select distinct(nip_anggota), tahun from tb_manggota union all select distinct(nip_ketua), tahun from tb_mketua;
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET done = 1;
OPEN cur1;
set jum = 0;
REPEAT
FETCH cur1 INTO nip, yr;
IF yr = old.tahun THEN
set jum=jum+1;
END IF;
UNTIL done END REPEAT;
CLOSE cur1;
set jum=jum-1;
update tb_dwh_pengabdian set pengabdian_jum_dosen_mengabdi = jum where pengabdian_tahun=old.tahun;
END;
$$
DELIMITER ;
The Red Row of the syntax is a row definiion, then a fetch (something we said to cut per row piece). And at the Green Line, you can find that if the table change on field year has a similar value with a cursor fetch, do something.
That is a simple example of using cursor in In MySQL PLSQL, Using Cursor in a Trigger.
Below i have a simple MySQLTrigger to show how cursor can be use. I use MySQL version 5.1.33.
Please Just See A Red Row of the Program, That i will Explain.
DELIMITER $$
DROP TRIGGER /*!50032 IF EXISTS */ `db_pengabdian`.`update_jum_pengabdi`$$
CREATE
/*!50017 DEFINER = 'root'@'localhost' */
TRIGGER `update_jum_pengabdi` AFTER UPDATE ON `tb_mketua`
FOR EACH ROW BEGIN
DECLARE done INT DEFAULT 0;
DECLARE nip CHAR(30);
DECLARE yr YEAR;
DECLARE jum INT;
DECLARE cur1 CURSOR FOR select distinct(nip_anggota), tahun from tb_manggota union all select distinct(nip_ketua), tahun from tb_mketua;
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET done = 1;
OPEN cur1;
set jum = 0;
REPEAT
FETCH cur1 INTO nip, yr;
IF yr = old.tahun THEN
set jum=jum+1;
END IF;
UNTIL done END REPEAT;
CLOSE cur1;
set jum=jum-1;
update tb_dwh_pengabdian set pengabdian_jum_dosen_mengabdi = jum where pengabdian_tahun=old.tahun;
END;
$$
DELIMITER ;
The Red Row of the syntax is a row definiion, then a fetch (something we said to cut per row piece). And at the Green Line, you can find that if the table change on field year has a similar value with a cursor fetch, do something.
That is a simple example of using cursor in In MySQL PLSQL, Using Cursor in a Trigger.
After Read a Post about Safely Backup MySQL Database With SQL Yog,
Below is the step by step we doing a MySQL Database backup with SQL Yog :
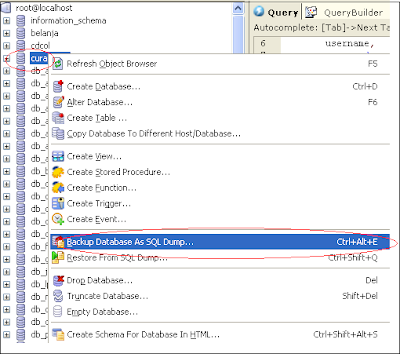
1. Right Click A Database
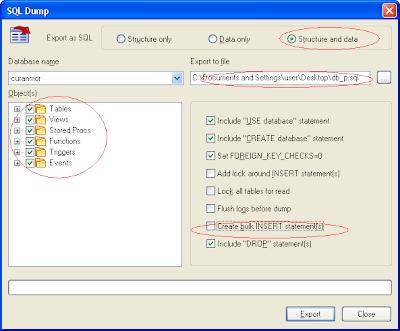
3. Choose Backup Options
4. Export and done.
The Explanation of Figure 2
Bulk SQL Statement and Non Bulk Insert Statement
andBackup MySQL Database Safely as SQL File with SQL Yog
Below is the step by step we doing a MySQL Database backup with SQL Yog :
1. Right Click A Database

Figure 1.
2. Choose Back Up Database3. Choose Backup Options
4. Export and done.
The Explanation of Figure 2
- All Check on table, stored procedure and trigger mean The backup doing all backup include table, views, stored procedure, trigger, event and function
- Structure and Data Check mean The Backup doing a Data and Structure Backup.
- File Name is a Must.
- Do not Check Use Bulk Insert Statement if you have a database that has great size.
Please pay attention to the MySQL SQL Insert Into Ststement below :
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (1,'Sambutan');
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (2,'Visi dan Misi');
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (3,'Roadmap penelitian Unud');
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (4,'Kebijakan penelitian Unud');
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (5,'TOR penelitian Unud');
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (6,'Tatalaksana penelitian');
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (7,'Kontak');
and MySQL SQL Insert Into Ststement below :
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (1,'Sambutan'),(2,'Visi dan Misi'),(3,'Roadmap penelitian Unud'),(4,'Kebijakan penelitian Unud'),(5,'TOR penelitian Unud'),(6,'Tatalaksana penelitian'),(7,'Kontak');
The First Statement is Call Non Bulk SQL Insert Statement, and The Second is Bulk SQL Insert Statement. This Bulk SQL Insert Statement can increase potential of Restore Database Error. A big size of database can cause a out of memory while Execute BULK Insert Statement. A Non Bulk Insert Statement can reduce potential of Restore Database Error, because it execute using smaller memory size and per single Table Row.
So I Recommend you to use Non Bulk SQL Insert Statement, even if the SQL Filesize can be bigger, the safety is more Important.
How can we provide a SQL File that contain Non Bulk SQL Insert Statement,
the simple way can be found Here
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (1,'Sambutan');
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (2,'Visi dan Misi');
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (3,'Roadmap penelitian Unud');
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (4,'Kebijakan penelitian Unud');
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (5,'TOR penelitian Unud');
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (6,'Tatalaksana penelitian');
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (7,'Kontak');
and MySQL SQL Insert Into Ststement below :
insert into `m_statis`(`idstatis`,`jenisstatis`) values (1,'Sambutan'),(2,'Visi dan Misi'),(3,'Roadmap penelitian Unud'),(4,'Kebijakan penelitian Unud'),(5,'TOR penelitian Unud'),(6,'Tatalaksana penelitian'),(7,'Kontak');
The First Statement is Call Non Bulk SQL Insert Statement, and The Second is Bulk SQL Insert Statement. This Bulk SQL Insert Statement can increase potential of Restore Database Error. A big size of database can cause a out of memory while Execute BULK Insert Statement. A Non Bulk Insert Statement can reduce potential of Restore Database Error, because it execute using smaller memory size and per single Table Row.
So I Recommend you to use Non Bulk SQL Insert Statement, even if the SQL Filesize can be bigger, the safety is more Important.
How can we provide a SQL File that contain Non Bulk SQL Insert Statement,
the simple way can be found Here
Database Programmer Usually Backup MySQL Database Safely as SQL File with SQL Yog. Because it was desktop software and user friendly. Backup MySQL Database Safely as SQL File with SQL Yog sometimes not safe causing by wide database.
The Backup of MySQL Database can be Safely if we don't use Bulk Insert Query, I mean a single Insert into Query to perform a inserting table.
How we do not use bulk insert in Database Backup?
Simply release check at the backup process.

This manner can reduce potential of Restore Database Error. A big size of database can cause a out of memory while using BULK Insert Statement.
A Brief Explanation of BULK SQL Insert Statement and Non BULK SQL Insert Statement
can be Found Here
The Backup of MySQL Database can be Safely if we don't use Bulk Insert Query, I mean a single Insert into Query to perform a inserting table.
How we do not use bulk insert in Database Backup?
Simply release check at the backup process.

This manner can reduce potential of Restore Database Error. A big size of database can cause a out of memory while using BULK Insert Statement.
A Brief Explanation of BULK SQL Insert Statement and Non BULK SQL Insert Statement
can be Found Here
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)