With iptraf we know how much traffic in and traffic out in our machine. How we use it below is the step by step.
1. Open Terminal in Fedora Core
2. Simply write iptraf and Choose Detail Interface Statistic
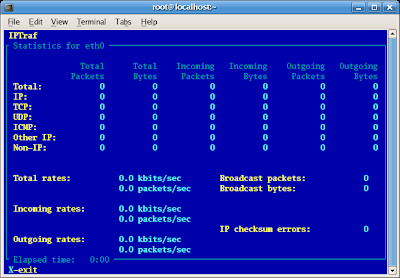
In Picture Above Mean iptraf catch no traffic in and no traffic out with all value is
Zero3. Try to ping another machine / computer like this picture below.
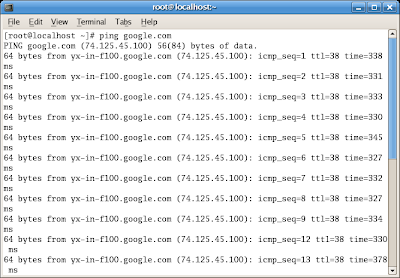
Ping cause a traffic out (sends / request) and traffic in (repply), so the value of indicator can be view in iptraf like pictute below :
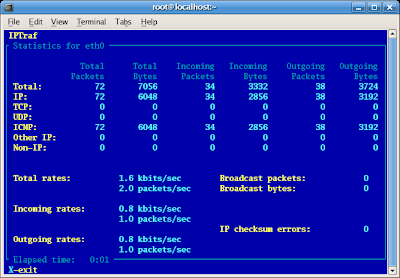
That was how we can use iptraf in Fedora Core.
MUD stands for Multi User Dimension. MUDs, and their variations listed above, are multi-user virtual reality games based on simulated worlds. Traditionally text based, graphical MUDs now exist. There are MUDs of all kinds on the Internet, and many can be joined free of charge.
Chat programs allow users on the Internet to communicate with each other by typing in real time. They are sometimes included as a feature of a Web site, where users can log into the "chat room" to exchange comments and information about the topics addressed on the site. Chat may take other, more wide-ranging forms. For example, America Online is well known for sponsoring a number of topical chat rooms.
Internet Relay Chat (IRC) is a service through which participants can communicate to each other on hundreds of channels. These channels are usually based on specific topics. While many topics are frivolous, substantive conversations are also taking place. To access IRC, you must use an IRC software program.
A variation of chat is the phenomenon of instant messenging. With instant messenging, a user on the Web can contact another user currently logged in and type a conversation. Most famous is America Online's Instant Messenger. ICQ, MSN and Yahoo are other commonly-used chat programs.
FAQ stands for Frequently Asked Questions. These are periodic postings to Usenet newsgroups that contain a wealth of information related to the topic of the newsgroup. Many FAQs are quite extensive. FAQs are available by subscribing to individual Usenet newsgroups. A Web-based collection of FAQ resources has been collected by The Internet FAQ Consortium and is available at /http://www.faqs.org/.
RFC stands for Request for Comments. These are documents created by and distributed to the Internet community to help define the nuts and bolts of the Internet. They contain both technical specifications and general information.
FYI stands for For Your Information. These notes are a subset of RFCs and contain information of interest to new Internet users.
Links to indexes of all three of these information resources are available on the University Libraries Web site at
http://library.albany.edu/reference/faqs.html
Usenet News is a global electronic bulletin board system in which millions of computer users exchange information on a vast range of topics. The major difference between Usenet News and e-mail discussion groups is the fact that Usenet messages are stored on central computers, and users must connect to these computers to read or download the messages posted to these groups. This is distinct from e-mail distribution, in which messages arrive in the electronic mailboxes of each list member.
Usenet itself is a set of machines that exchanges messages, or articles, from Usenet discussion forums, called newsgroups. Usenet administrators control their own sites, and decide which (if any) newsgroups to sponsor and which remote newsgroups to allow into the system.
There are thousands of Usenet newsgroups in existence. While many are academic in nature, numerous newsgroups are organized around recreational topics. Much serious computer-related work takes place in Usenet discussions. A small number of e-mail discussion groups also exist as Usenet newsgroups.
The Usenet newsfeed can be read by a variety of newsreader software programs. For example, the Netscape suite comes with a newsreader program called Messenger. Newsreaders are also available as standalone products.
One of the benefits of the Internet is the opportunity it offers to people worldwide to communicate via e-mail. The Internet is home to a large community of individuals who carry out active discussions organized around topic-oriented forums distributed by e-mail. These are administered by software programs. Probably the most common program is the listserv.
A great variety of topics are covered by listservs, many of them academic in nature. When you subscribe to a listserv, messages from other subscribers are automatically sent to your electronic mailbox. You subscribe to a listserv by sending an e-mail message to a computer program called a listserver. Listservers are located on computer networks throughout the world. This program handles subscription information and distributes messages to and from subscribers. You must have a e-mail account to participate in a listserv discussion group. Visit Tile.net at /http://tile.net/ to see an example of a site that offers a searchablecollection of e-mail discussion groups.
FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. This is both a program and the method used to transfer files between computers. Anonymous FTP is an option that allows users to transfer files from thousands of host computers on the Internet to their personal computer account. FTP sites contain books, articles, software, games, images, sounds, multimedia, course work, data sets, and more.
If your computer is directly connected to the Internet via an Ethernet cable, you can use one of several PC software programs, such as WS_FTP for Windows, to conduct a file transfer.
FTP transfers can be performed on the World Wide Web without the need for special software. In this case, the Web browser will suffice. Whenever you download software from a Web site to your local machine, you are using FTP. You can also retrieve FTP files via search engines such as FtpFind, located at /http://www.ftpfind.com/. This option is easiest because you do not need to know FTP program commands.
Telnet is a program that allows you to log into computers on the Internet and use online databases, library catalogs, chat services, and more. There are no graphics in Telnet sessions, just text. To Telnet to a computer, you must know its address. This can consist of words (locis.loc.gov) or numbers (140.147.254.3). Some services require you to connect to a specific port on the remote computer. In this case, type the port number after the Internet address. Example: telnet nri.reston.va.us 185.
Telnet is available on the World Wide Web. Probably the most common Web-based resources available through Telnet have been library catalogs, though most catalogs have since migrated to the Web. A link to a Telnet resource may look like any other link, but it will launch a Telnet session to make the connection. A Telnet program must be installed on your local computer and configured to your Web browser in order to work.
With the increasing popularity of the Web, Telnet has become less frequently used as a means of access to information on the Internet.
Electronic mail, or e-mail, allows computer users locally and worldwide to exchange messages. Each user of e-mail has a mailbox address to which messages are sent. Messages sent through e-mail can arrive within a matter of seconds.
A powerful aspect of e-mail is the option to send electronic files to a person's e-mail address. Non-ASCII files, known as binary files, may be attached to e-mail messages. These files are referred to as MIME attachments.MIME stands for Multimedia Internet Mail Extension, and was developed to help e-mail software handle a variety of file types. For example, a document created in Microsoft Word can be attached to an e-mail message and retrieved by the recipient with the appropriate e-mail program. Many e-mail programs, including Eudora, Netscape Messenger, and Microsoft Outlook, offer the ability to read files written in HTML, which is itself a MIME type.
The World Wide Web (abbreviated as the Web or WWW) is a system of Internet servers that supports hypertext to access several Internet protocols on a single interface. Almost every protocol type available on the Internet is accessible on the Web. This includes e-mail, FTP, Telnet, and Usenet News. In addition to these, the World Wide Web has its own protocol: HyperText Transfer Protocol, or HTTP. These protocols will be explained later in this document.
The World Wide Web provides a single interface for accessing all these protocols. This creates a convenient and user-friendly environment. It is no longer necessary to be conversant in these protocols within separate, command-level environments. The Web gathers together these protocols into a single system. Because of this feature, and because of the Web's ability to work with multimedia and advanced programming languages, the Web is the fastest-growing component of the Internet.
The operation of the Web relies primarily on hypertext as its means of information retrieval. HyperText is a document containing words that connect to other documents. These words are called links and are selectable by the user. A single hypertext document can contain links to many documents. In the context of the Web, words or graphics may serve as links to other documents, images, video, and sound. Links may or may not follow a logical path, as each connection is programmed by the creator of the source document. Overall, the Web contains a complex virtual web of connections among a vast number of documents, graphics, videos, and sounds.
Producing hypertext for the Web is accomplished by creating documents with a language called HyperText Markup Language, or HTML. With HTML, tags are placed within the text to accomplish document formatting, visual features such as font size, italics and bold, and the creation of hypertext links. Graphics and multimedia may also be incorporated into an HTML document. HTML is an evolving language, with new tags being added as each upgrade of the language is developed and released. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), led by Web founder Tim Berners-Lee, coordinates the efforts of standardizing HTML. The W3C now calls the language XHTML and considers it to be an application of the XML language standard.
The World Wide Web consists of files, called pages or home pages, containing links to documents and resources throughout the Internet.
The Web provides a vast array of experiences including multimedia presentations, real-time collaboration, interactive pages, radio and television broadcasts, and the automatic "push" of information to a client computer. Programming languages such as Java, JavaScript, Visual Basic, Cold Fusion and XML are extending the capabilities of the Web. A growing amount of information on the Web is served dynamically from content stored in databases. The Web is therefore not a fixed entity, but one that is in a constant state of development and flux.
The Internet is a computer network made up of thousands of networks worldwide. No one knows exactly how many computers are connected to the Internet. It is certain, however, that these number in the millions.
No one is in charge of the Internet. There are organizations which develop technical aspects of this network and set standards for creating applications on it, but no governing body is in control. The Internet backbone, through which Internet traffic flows, is owned by private companies.
All computers on the Internet communicate with one another using the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol suite, abbreviated to TCP/IP. Computers on the Internet use a client/server architecture. This means that the remote server machine provides files and services to the user's local client machine. Software can be installed on a client computer to take advantage of the latest access technology.
An Internet user has access to a wide variety of services: electronic mail, file transfer, vast information resources, interest group membership, interactive collaboration, multimedia displays, real-time broadcasting, shopping opportunities, breaking news, and much more.
The Internet consists primarily of a variety of access protocols. Many of these protocols feature programs that allow users to search for and retrieve material made available by the protocol.
Banyak orang mempertanyakan mengapa kita sulit-sulit mempelajari Pengolahan Citra Digital di Masa Kuliah. Kuliah Pengolahan Citra Digital ini hanya mata kuliah khusus di bidang Studi Teknik Informatika, Teknik Elektro, MIPA dan Antariksa.
Peluang Kerja Bidang Pengolahan Citra terfokus pada instansi-instansi tertentu seperti Medis (Citra-citra pemeriksaan Alat-alat Kedokteran), Pemerintahan (Aplikasi Pengenalan Diri / Biometrika), bahkan bidang Pencitraan satelit dan Antariksa.
Sebagian Bidang Pengolahan Citra juga dapat dimanfaatkan untuk kemampuan grafis untuk pengolahan foto untuk mendapatkan foto yang lebih attraktif. Beberapa teknik yang sering digunakan diantaranya :
Image Adjustment dan
Image Filter.

Gambar
Grayscale, salah satu contoh sederhana Pengolahan Citra (
Image Adjustment).
Sosrobahu adalah teknik pembuatan jalan layang untuk menghindari kemacetan. Teknik ini ditemukan oleh Dr. Ir. Cokorda Raka Sukawati.

sumber gambar: http://www.depperin.go.id/data/industry/promotion/pic_4.htm
Teknik ini berdasarkan pemutaran beton yang disangga tiang besar. Menurut Dr. Ir. Cokorda Raka Sukawati, berat beton-beton yang diputar mencapai berat 480 Ton. Pemutaran dilakukan dengan tekanan minyak bernilai 78 kg per cm2.
Penemuan ini mengangkat prestasi konstruksi di Indonesia pada Era 80-an. Suatu yang patut dibanggakan
Pemilu Indonesia 2009 dalam juga memanfaatkan teknologi WEBGIS (
Geograpic Information System / Sistem Informasi Geografis). Teknologi yang dimanfaatkan ini bertujuan menampilkan sebaran Suara Partai Politik di Seluruh Wilayah Pemilihan di Indonesia. Website WEBGIS ini tentunya sangat bermanfaat. Fungsi-fungsi WEBGIS diantaranya ditunjukkan olah gambar-gambar berikut :
Gambar 1 Menunjukkan Peta Konsentrasi Partai Politik

Gambar 2 adalah lanjutan gambar 1

Gambar 3 Menunjukkan Sebaran Suara Terbanyak.

Ayo Terus Maju Penggunaan Teknologi Indonesia!!
Kita dapat mengetahui langsung hasil Real Count KPU terkait suara terhadap Pemilu legislatif 2009 di
website KPU pada link
Tabulasi Nasional.
Kira kira kita dapat melihat grafik tabulasi seperti gambar berikut :

Hebat Pemilu sekarang sudah memanfaatkan teknologi komputerisasi terkini. Semua serba cepat dan tepat. Sukses selalu buat Indonesia!!
Style sheets merupakan unsur yang sangat penting dalam membuat dynamic HTML. Meskipun bukan merupakan suatu keharusan dalam membuat web, akan tetapi penggunaan style sheets merupakan kelebihan tersendiri. Suatu style sheet merupakan tempat dimana anda mengontrol dan memanage style-style yang ada. Style sheet mendeskripsikan bagaiman tampilan document HTML di layar. Dapat disebut juga sebagai template dari documents HTML yang menggunakanya.
Misalnya membuat efek-efek spesial di web dengan menggunakan style sheet.
Secara teoritis bisa menggunakan style sheet technology dengan HTML, akan tetapi pada prakteknya hanya Cascading Style Sheet (CSS) technology yang support pada hampir semua web Browser. Karena CSS telah di standardkan oleh World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) untuk di gunakan di web browser.
Inline stylesAda dua cara yang bisa digunakan untuk merubah style dari web page, yaitu dengan :
- Merubah inline style
- Menulis script untuk merubah style.
Dengan meggunakan inline style anda dapat membuat dynamic style tanpa harus menambahkan script ke web. Inline styles merupakan style yang bisa dipasang pada element web tertentu saja. Contohnya adalah jika ingin menambahkan style pada
Dengan meggunakan inline style anda dapat membuat dynamic style tanpa harus menambahkan script ke web. Inline styles merupakan style yang bisa dipasang pada element web tertentu saja. Contohnya adalah jika ingin menambahkan style pada <H1> dengan warna merah, harus mengeset attribut STYLE dari tag <H1>.
<H1 STYLE=”color:red”>
jika ingin menggunakan script untuk memodifikasi inline style, dapat menggunakan Style Object. Style Object mensupport semua property yang di support CSS untuk style. Untuk menggunakan property pada script :
- Hilangkan tanda hubung “-” dari property CSS Style
- Ganti huruf setelah tanda hubung menjadi Capital.
Contoh adalah dengan mengganti font-weight menjadi fontWeight, dan mengubah text-align menjadi textAlign.
Istilah-istilah dalam style sheet
a. Style ruleCascading style sheet merupakan kumpulan aturan yang mendefinisikan style dari document. Sebagai contoh, membuat aturan style yang menentukan bahwa semua <H2> di tampilkan dengan warna orange.
b. Style sheetStyle sheet dapat dapat di embedded ke HTML document. Atau disebut embedded style sheet. Style sheet juga bisa dibuat sebagai external file dan di link ke document HTML. Style role bisa di kenakan pada bagian tertentu dari web page. Sebagai contoh, menentukan paragraph tertentu di tampilkan dengan style bold dan italic sementara yang lain tetap seperti biasa.
c. SelectorPada style sheet, terdiri dari dua bagian, yaitu selector dan declaration. Selector merupakan bagian pertama sebelum dideklarasikan selector {declaration}.
selector { property1: value; property2:value, . . .}
H1{ color:green; background-color:orange}
d. Komentar dalam style sheetsComments atau komentar biasanya di gunakan oleh programmer untuk memudahkan mengingat kembali script yang sudah di tulisnya, Comments di CSS hampir sama dengan comments di C atau C++ yaitu dengan menggunakan:
/* isi Comments */
Contoh:
H1 { color:blue;} /* H1 elements akan menjadi biru */
Tags.H1.color = “blue”; /* H1 elements akan menjadi biru */
e. �Link ke sheet lainnyaApabila menginginkan style yang sama untuk halaman HTML yang lain, disarankan memperguakan sheet-sheet terpisah namun satu dan lainnya terhubung dengan cara link. Dapat mengikuti cara berikut ini :
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
Kode tag untuk link ini ditempatkan di bagian "head" dokumen. Perintah rel perlu diatur dengan pernyataan "stylesheet" agar supaya browser dapat menemukan perintah href sebagai penunjukan ke alamat Web (URL) sheet.
PHP adalah bahasa scripting yang menyatu dengan HTML dan dijalankan pada server side. Artinya semua sintaks yang diberikan akan sepenuhnya dijalankan pada server sedangkan yang dikirimkan ke browser hanya hasilnya saja. Berikut ini beberapa dasar-dasar pemrograman menggunakan PHP:
VariableDalam PHP setiap nama variable diawali tanda dollar ($). Misalnya nama variable a dalam PHP ditulis dengan $a. Jenis suatu variable ditentukan pada saat jalannya program dan tergantung pada konteks yang digunakan.
Struktur kontrolStuktur kontrol ifKonstruksi if digunakan untuk melakukan eksekusi suatu statement yang bersyarat. Cara penulisannya adalah sebagai berikut:
if (syarat)
{
statement
}
atau:
if (syarat)
{
statement
}
else
{
statement lain
}
Statemen kontrol while Bentuk dasar dari statement While adalah sebagai berikut:
while (syarat)
{
statement
}
Arti dari statemant While adalah memberikan perintah untuk menjalankan statement dibawahnya secara berulang-ulang, selama syaratnya terpenuhi.
Statemen kontrol whileCara penulisan statement FOR adalah sebagai berikut:
for (ekspresi1; ekspresi2 ; ekspresi3)
{
statement
}
ekspresi1 menunjukkan nilai awal untuk suatu variable ekspresi2 menunjukkan syarat yang harus terpenuhi untuk menjalankan statemant ekspresi3 menunjukkan pertambahan nilai untuk suatu variable
Statemen kontrol switchStatement SWITCH digunakan untuk membandingkan suatu variable dengan beberapa nilai serta menjalankan statement tertentu jika nilai variable sama dengan nilai yang dibandingkan.
Struktur Switch adalah sebagai berikut:
switch (variable)
case nilai:
statement
case nilai:
statemant
.
.
Statemen kontrol requireStatement Require digunakan untuk membaca nilai variable dan fungsi-fungsi dari sebuah file lain. Cara penulisan statement require adalah:
require(namafile);
Statement Require ini tidak dapat dimasukkan diadalam suatu struktur looping misalnya while atau for. Karena hanya memperbolehkan pemangggilan file yang sama tersebut hanya sekali saja.
Statemen kontrol includeStatement Include akan menyertakan isi suatu file tertentu. Include dapat diletakkan didalam suatu looping misalkan dalam statement for atau while.
Eksistensi Lembaga Perkreditan Desa Adat secara prinsip diatur dalam Awig-Awig Desa Adat, sehingga mengikat seluruh masyarakat desa adatnya. Status dan penggunaan nama Lembaga Perkreditan Desa telah diatur dalam ketentuan yang ditetapkan oleh Pemerintah Daerah Tingkat I Propinsi Bali yaitu Peraturan Daerah Nomor 8 Tahun 2002 tentang Lembaga Perkreditan Desa yang dalam Pasal 2 Ayat (1) menyebutkan Lembaga Perkreditan Desa merupakan badan usaha keuangan milik desa yang melaksanakan kegiatan usaha di lingkungan desa dan untuk krama desa. (2) Masyarakat adat setempat maupun di luar desa adatnya dapat melakukan penyimpanan dana dan meminjam kredit pada Lembaga Perkreditan Desa Adat.
Pemberian kredit kepada masyarakat di luar desa adatnya telah bertentangan dengan Ketentuan dalam Pasal 7 Ayat (1) sub .b. Peraturan Daerah Nomor 8 Tahun 2002 yang menyebutkan memberikan pinjaman hanya kepada krama desa.
Kebijakan Pemerintah Indonesia dibidang Otonomi Daerah, telah berpengaruh secara nyata terhadap sistem pemerintahan dan keuangan. Dari sentralisasi kepada desentralisasi. Hal tersebut sesuai dengan UU Nomor 22 tahun 1999, dimana pemberian kewenangan otonomi daerah tersebut adalah dalam wujud otonomi yang luas, nyata dan bertanggung jawab, termasuk dalam hal ini terutama adalah kewenangan dalam desentralisasi fiskal sebagaimana diatur dalam UU Nomor 25 tahun 1999.
Penerapan kebijakan desentralisasi fiskal mengandung suatu implikasi bahwa transfer dana ke daerah melalui dana perimbangan menunjukkan jumlah yang semakin besar, sehingga kemampuan keuangan daerah meningkat disertai dengan peningkatan kewenangan dalam pengelolaannya.
Dampak dari kebijakan otonomi daerah telah menimbulkan peluang peningkatan kegiatan perekonomian daerah, terutama di daerah luar Jawa, yang selama ini mengalami ketinggalan dibanding Jakarta atau Jawa. Kegiatan bisnis daerah yang semakin berkembang tersebut pada gilirannya akan menarik investor untuk menanamkan modalnya di daerah, termasuk dalam hal ini adalah lembaga keuangan mikro dan perbankan. Kehadiran mereka diharapkan akan semakin meningkatkan bisnis daerah yang bersangkutan, melalui berbagai produk yang ditawarkannya.
Saat ini telah muncul bahasa generasi selanjutnya dari HTML yaitu XHTML (X-tensible HTML). Struktur XHTML ini pada prinsipnya hampir sama dengan HTML, hanya lebih terstruktur dan konsisten.
Berikut ini beberapa perbedaan antara HTML dan XHTML.
- Dalam HTML, penggunaan tag <html>, <head>, <body>, DOCTYPE tidak ada pengaruhnya, artinya dalam HTML tag-tag tersebut sifatnya optional (boleh ada, boleh tidak) dan tidak berpengaruh pada tampilan di browser. Namun dalam XHTML tag-tag tersebut harus ada. Apabila ketentuan tersebut dilanggar, maka akan terjadi efek tertentu pada tampilan di browser.
- Dalam HTML, tag-tag penutup misalnya </p> atau </i> dll, sifatnya optional. Namun pada XHTML tag penutup harus ada.
- Dalam HTML tag-tag yang berdiri sendiri (tanpa tag penutup), misalnya <img src="image.jpg"> tidak ada slash penutup. Sedangkan dalam XHTML slash penutup harus ada, misal <img src="image.jpg" />.
- Dalam HTML, nilai semua atribut dalam tag tidak harus diapit dengan tanda petik ganda (double quote), misal penulisan <img src=image.jpg alt=gambar> diperbolehkan. Namun dalam XHTML double quote harus mengapit nilai atribut, misal <img src="image.jpg" alt="gambar">.
- Dalam HTML penulisan semua tag boleh dalam huruf besar atau huruf kecil, misal <HEAD>. Namun dalam XHTML semua tag harus ditulis dalam huruf kecil, misal <head>.
- Dalam HTML, nilai yang sama dengan atribut akan diabaikan, misal <hr width=70% noshade>. Artinya dalam HTML untuk nama atribut yang sama dengan nilainya dapat ditulis dalam satu nama saja. Namun dalam XHTML, semua atribut dan nilai harus dinyatakan secara eksplisit, misal <hr width="70%" noshade="noshade">.
Melihat perbedaan-perbedaan di atas, maka XHTML sangat disarankan bagi desainer web yang menginginkan konsistensi dalam struktur konten halaman webnya. Selain itu, XHTML lebih kompatible untuk diintegrasikan dengan CSS (Cascade Style Sheet) dibandingan dengan HTML.
 In Picture Above Mean iptraf catch no traffic in and no traffic out with all value is Zero
In Picture Above Mean iptraf catch no traffic in and no traffic out with all value is Zero








